Q1. What are Non-Banking Financial companies (NBFCs) and how it works?
A Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is a financial institution that provides banking services such as loans and advances, investments, leasing, hire-purchase, insurance, and other financial products and services without having a banking license.
NBFCs can raise funds from various sources such as deposits, bonds, debentures, and commercial paper, among others. They lend money to individuals and businesses for various purposes, such as buying a house, purchasing a car, starting a business, or funding working capital requirements.
Q2. How it was Incorporated? How did it become popular in the financial society?
Overall, NBFCs have become popular in the financial society because of their flexibility, innovation, and ability to cater to the diverse financial needs of the economy. They have played a crucial role in financial inclusion and poverty alleviation and have contributed significantly to the growth of the Indian financial sector.
ROLE OF NON-BANKING FINANCIAL COMPANIES (NBFCs)

It plays a vital role in the Indian financial sector by providing credit and other financial services to the underserved and unbanked sectors of the economy. Some of the key roles played by NBFCs are:
- Providing credit: NBFCs provide credit to individuals, small businesses, and other entities for various purposes such as buying a house, purchasing a car, funding working capital requirements, and starting a business.
- Promoting financial inclusion: NBFCs have played a crucial role in promoting financial inclusion by providing credit and other financial services to low-income households, rural and semi-urban areas, and other underserved and unbanked segments of the population.
- Offering customized financial products and services: NBFCs offer customized financial products and services to their customers based on their specific needs and requirements. This has allowed them to serve segments of the economy that are not adequately served by banks.
- Enhancing competition: NBFCs have enhanced competition in the financial sector by offering innovative products and services, which has put pressure on banks to improve their offerings and services.
- Supporting the government’s initiatives: NBFCs have supported the government’s initiatives such as financial inclusion, affordable housing, and microfinance by providing credit and other financial services to the targeted beneficiaries.
They have played a crucial role in financial inclusion and poverty alleviation and have contributed significantly to the growth of the Indian financial sector.
Q3. How much interest rate will charge on the loan and advances by NBFCs?
The interest rates charged by NBFCs on loans and advances vary based on several factors such as the type of loan, creditworthiness of the borrower, loan amount, and loan tenure. Generally, the interest rates charged by NBFCs are higher than those offered by banks due to their higher risk profile and cost of funds.
The interest rates charged by NBFCs can range from as low as 8% to as high as 30% or more, depending on the factors mentioned above. For example, the interest rate on personal loans offered by NBFCs can range from 10% to 30%.
It is important to note that the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regulates the interest rates charged by NBFCs to ensure that they are fair and reasonable. The RBI has issued guidelines on the interest rates charged by NBFCs, and it is mandatory for them to disclose the interest rates and other charges upfront to their customers.
Therefore, it is advisable to compare the interest rates and other charges offered by different NBFCs before taking a loan or advance to ensure that you get the best deal based on your financial situation and requirements.
Q4. What are the documents required for taking services from NBFC Company?
ROLE OF NON-BANKING FINANCIAL COMPANIES (NBFCs)

To register as an NBFC company in India, the following steps need to be followed:
Step 1: Incorporation of the company: The first step is to incorporate a company under the Companies Act, 2013 or any other relevant law. The company can be registered as a private or public limited company with a minimum paid-up capital of Rs. 2crore.
Step 2: Obtain the NBFC license: The next step is to apply for the NBFC license from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). The application can be made online through the RBI’s website, and it must be accompanied by the necessary documents, such as the company’s memorandum and articles of association, certificate of incorporation, and details of the directors and shareholders.
Step3: Submit the documents: Once the application is made, the company needs to submit the necessary documents to the RBI for verification. The documents may include the company’s audited financial statements, KYC documents of the directors, and other relevant documents.
Step 4: Compliance with RBI guidelines: After the NBFC license is issued, the company must comply with the guidelines and regulations prescribed by the RBI. These guidelines include maintaining adequate capital adequacy ratio, ensuring compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) norms, and submitting periodic reports to the RBI.
Step 5: Ongoing compliance: The NBFC Company must ensure ongoing compliance with the regulations and guidelines prescribed by the RBI, such as submission of periodic reports and maintaining adequate capital adequacy ratio.


ADVANTAGES:
- Access to credit: NBFCs provide credit facilities to borrowers who may not be eligible for loans from traditional banks due to a lack of collateral or credit history. They help bridge the credit gap and provide access to credit to a wider range of borrowers.
- Faster loan processing: NBFCs have streamlined loan processing systems that enable them to process loan applications faster than traditional banks. This allows borrowers to get access to credit quickly and efficiently.
- Flexibility: NBFCs offer flexible loan terms and repayment options to borrowers. They cater to specific requirements of borrowers such as seasonal fluctuations in income, which may not be accommodated by traditional banks.
- Diverse products and services: NBFCs offer a wide range of financial products and services such as personal loans, business loans, leasing, factoring, and insurance. This enables them to cater to the diverse financial needs of borrowers and investors.
- Financial inclusion: NBFCs have a wider reach in rural and semi-urban areas, where traditional banks may not have a significant presence. This enables them to provide credit facilities to people in these areas and contribute to financial inclusion.
- Investment opportunities: NBFCs offer investment opportunities to investors, including fixed deposits, bonds, and other financial instruments. They provide higher returns on investment than traditional bank deposits, making them an attractive investment option for investors.
- Support to small and medium enterprises: NBFCs provide credit facilities to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and help them meet their working capital requirements.
DISADVANTAGES:
- Higher interest rates: NBFCs typically charge higher interest rates compared to traditional banks. This is because they cater to borrowers who may not have a credit history or collateral, which increases the risk of default.
- Lack of deposit insurance: NBFCs do not offer deposit insurance to their customers. This means that if an NBFC goes bankrupt, customers may lose their deposits.
- Limited regulatory oversight: While NBFCs are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the level of oversight is lower compared to traditional banks. This can increase the risk of fraudulent practices and mismanagement.
- Reputation risk: NBFCs may be subject to reputation risk, especially if they engage in unethical or fraudulent practices. This can damage their reputation and make it difficult for them to raise capital or attract customers in the future.
- Concentration of risk: NBFCs may concentrate their lending in specific sectors or industries, which can increase their exposure to sector-specific risks. This can make them vulnerable to economic downturns or industry-specific shocks.
TYPES OF NON-BANKING FINANCIAL COMPANIES
To register as an NBFC company in India, the following steps need to be followed:
Step 1: Incorporation of the company: The first step is to incorporate a company under the Companies Act, 2013 or any other relevant law. The company can be registered as a private or public limited company with a minimum paid-up capital of Rs. 2crore.
Step 2: Obtain the NBFC license: The next step is to apply for the NBFC license from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). The application can be made online through the RBI’s website, and it must be accompanied by the necessary documents, such as the company’s memorandum and articles of association, certificate of incorporation, and details of the directors and shareholders.
Step3: Submit the documents: Once the application is made, the company needs to submit the necessary documents to the RBI for verification. The documents may include the company’s audited financial statements, KYC documents of the directors, and other relevant documents.
Step 4: Compliance with RBI guidelines: After the NBFC license is issued, the company must comply with the guidelines and regulations prescribed by the RBI. These guidelines include maintaining adequate capital adequacy ratio, ensuring compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) norms, and submitting periodic reports to the RBI.
Step 5: Ongoing compliance: The NBFC Company must ensure ongoing compliance with the regulations and guidelines prescribed by the RBI, such as submission of periodic reports and maintaining adequate capital adequacy ratio.
- Asset Finance Company (AFC): AFCs provide loans and leasing facilities for purchasing assets such as machinery, equipment, and vehicles.
- Investment Company (IC): ICs primarily invest in shares, debentures, and other securities issued by the government or other organizations.
- Loan Company (LC): LCs provide loans and advances to individuals and companies.
- Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC): IFCs provide long-term finance for infrastructure projects such as roads, ports, airports, and power plants
- Systematically Important Non-Deposit Taking Company (NBFC-ND-SI): These are NBFCs with an asset size of Rs. 500 crore or more. They are classified as systemically important as their failure could have a significant impact on the financial system.
- Microfinance Institution (MFI): MFIs provide financial services such as credit, savings, and insurance to low-income individuals and households.
- Non-Banking Financial Company – Factors (NBFC-Factors): These are NBFCs engaged in the factoring business. Factoring involves the purchase of accounts receivables from businesses at a discount.
- Non-Banking Financial Company – Housing Finance Company (NBFC-HFC): These are NBFCs engaged in the housing finance business. They provide long-term finance for purchasing or constructing homes.
- Non-Banking Financial Company – Non-Operative Financial Holding Company (NBFC-NOFHC): These are NBFCs that act as holding companies for subsidiaries engaged in financial services.

RULES AND REGULATIONS OF NON-BANKING FINANCIAL COMPANIES (NBFCs)
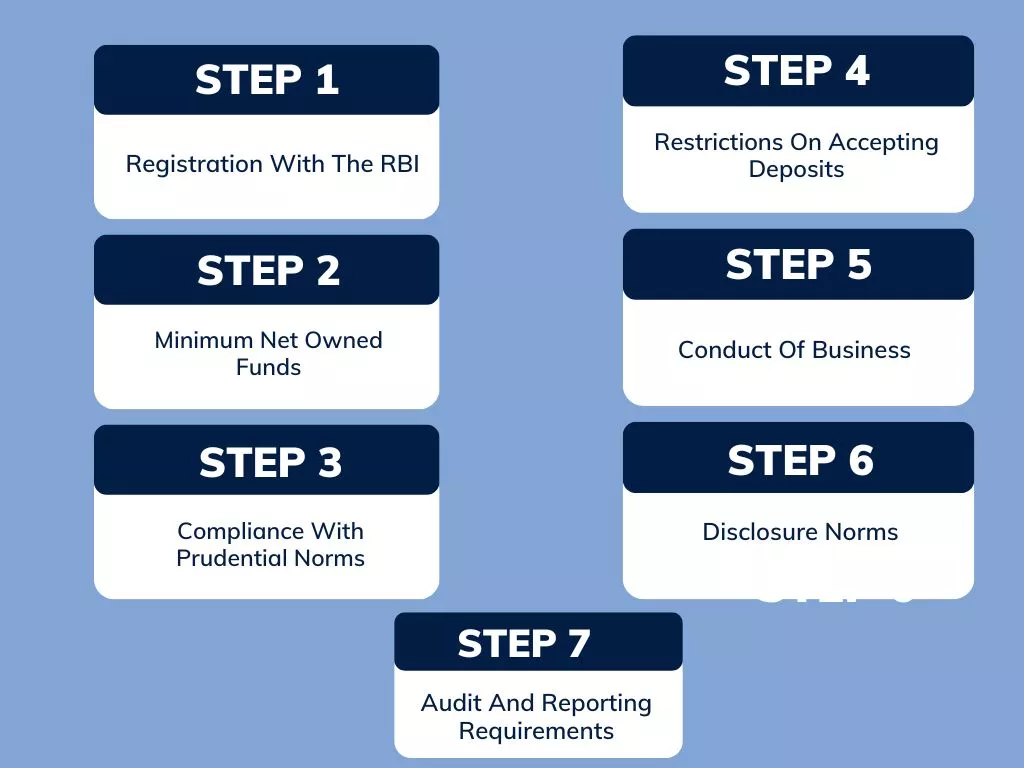
NBFCs in India are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) under the provisions of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- Registration with the RBI: All NBFCs in India are required to be registered with the RBI. The registration process involves the submission of various documents such as a certificate of incorporation, memorandum of association, and details of the directors and shareholders.
- Minimum net owned funds: NBFCs are required to maintain a minimum net owned fund (NOF) based on the type of business they are engaged in.
For example, NBFCs engaged in loan and investment activities are required to maintain an NOF of Rs. 2 crore.
- Compliance with prudential norms: NBFCs are required to comply with prudential norms such as maintaining adequate capital adequacy ratios (CAR), maintaining minimum liquidity ratios, and classifying assets into standard, sub-standard, doubtful, and loss categories.
- Restrictions on accepting deposits: NBFCs are not allowed to accept demand deposits from the public. However, they are allowed to accept fixed deposits for a minimum period of 12 months.
- Conduct of business: NBFCs are required to comply with various regulations related to the conduct of business such as the Fair Practices Code, Anti-Money Laundering (AML) guidelines, and Know Your Customer (KYC) norms.
- Disclosure norms: NBFCs are required to make various disclosures such as financial statements, annual reports, and information about the directors and shareholders. They are also required to disclose information about their business activities and risks.
- Audit and reporting requirements: NBFCs are required to get their financial statements audited by a qualified auditor and submit them to the RBI. They are also required to submit various reports such as the monthly return on prudential norms and the annual return on deposit-taking activities.
COMPLIANCES FOR NBFCs ON THE BASIS OF MONTHLY, QUARTERLY AND ANNUALLY RETURN
NBFCs are required to comply with various reporting requirements to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on a monthly, quarterly, and annual basis. Here are some of the major returns and reports that NBFCs are required to file:
- Monthly Return on Prudential Norms: NBFCs are required to file a monthly return on prudential norms with the RBI. This return provides information on the asset classification, income recognition, and provisioning norms followed by the NBFC.
- Quarterly Return on Capital Adequacy Ratio: NBFCs are required to maintain a minimum capital adequacy ratio (CAR) as per the guidelines issued by the RBI. NBFCs are required to file a quarterly return on their CAR with the RBI.
- Quarterly Return on Exposure to Real Estate Sector: NBFCs are required to file a quarterly return on their exposure to the real estate sector. This return provides information on the total amount of advances and investments made by the NBFC in the real estate sector.
- Annual Return on Deposit-Taking Activities: NBFCs that accept deposits from the public are required to file an annual return on their deposit-taking activities with the RBI. This return provides information on the total amount of deposits accepted and outstanding as on the last day of the financial year.
- Annual Audited Financial Statements: NBFCs are required to get their financial statements audited by a qualified auditor and submit them to the RBI on an annual basis. The audited financial statements should provide a true and fair view of the financial position of the NBFC as on the last day of the financial year.
Q5. What are the key compliances that NBFCs needs?
NBFCs are required to comply with various regulatory requirements and guidelines issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Some of the key compliances that NBFCs need to adhere to are:
- Registration and Licensing: NBFCs are required to obtain a certificate of registration from the RBI before commencing their business operations. NBFCs are also required to obtain a separate license from the RBI for certain activities such as accepting deposits from the public.
- Maintenance of Capital Adequacy Ratio: NBFCs are required to maintain a minimum capital adequacy ratio (CAR) as per the guidelines issued by the RBI. The minimum CAR for NBFCs is 15% of the risk-weighted assets.
- Compliance with Prudential Norms: NBFCs are required to comply with various prudential norms such as income recognition, asset classification, and provisioning norms. These norms are aimed at ensuring that NBFCs maintain adequate reserves to cover potential losses.
- Disclosure Requirements: NBFCs are required to disclose various information such as their financial statements, risk management policies, and other key information to the public and the RBI.
- Fair Practices Code: NBFCs are required to follow a Fair Practices Code (FPC) that outlines their policies and procedures for dealing with customers. The FPC covers areas such as loan appraisal and processing, disbursement of loans, customer grievance redressal, and recovery of dues.
- Credit Information Companies (CICs): NBFCs are required to become members of at least one Credit Information Company (CIC) to access credit information of their customers. NBFCs are also required to submit credit information of their customers to the CICs.
- KYC and AML Requirements: NBFCs are required to comply with Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) guidelines issued by the RBI to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Reporting Requirements: NBFCs are required to submit various reports and returns to the RBI on a regular basis. The reports cover areas such as prudential norms, capital adequacy, exposure to the real estate sector, deposit-taking activities, and audited financial statements.
- Minimum Net Owned Fund (NOF): NBFCs are required to maintain a minimum net owned fund (NOF) as per the guidelines issued by the RBI. The NOF requirement varies based on the type of NBFC and its activities.
Overall, NBFCs need to comply with various regulatory requirements and guidelines to ensure the stability and development of the sector, while safeguarding the interests of depositors and investors. Non-compliance with these regulations may lead to penalties and other legal consequences.



